In the ever-evolving world of technology, the introduction of 5G stands as a monumental leap forward. This fifth generation of mobile network technology promises to redefine the way we communicate, work, and even live. But what exactly is 5G, and why is it causing such a stir in the global communication landscape?
A Brief History of Mobile Networks
To truly appreciate the significance of 5G, it’s essential to take a brief journey through the evolution of mobile networks:
| Generation | Introduction Year | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| 1G | 1980s | Analog voice calls |
| 2G | Early 1990s | Digital voice and SMS |
| 3G | Early 2000s | Mobile data, video calling |
| 4G | 2010s | High-speed data, HD video streaming |
| 5G | 2020s | Ultra-fast data, IoT, low latency |
As the table illustrates, each generation brought about significant advancements, with 5G being the most transformative yet. While 4G focused on delivering high-speed data suitable for activities like video streaming, 5G aims to connect virtually everyone and everything, including machines, objects, and devices.
The Promise of 5G

5G is not just about speed, although it does promise to be up to 100 times faster than 4G. It’s about creating a more connected and responsive world. Here are some of the key promises of 5G:
- Ultra-reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC): With response times as low as 1 millisecond, 5G will enable real-time reactions, crucial for applications like autonomous driving and telemedicine.
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): This will cater to our ever-growing data needs, ensuring smoother experiences in data-intensive applications like virtual reality and 4K video streaming.
- Massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC): This will allow billions of devices to connect simultaneously, paving the way for a truly interconnected Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
The Basics of 5G Technology
5G, or fifth-generation technology, represents the latest iteration in the evolution of mobile networks. While its predecessors primarily focused on connecting people, 5G’s vision is broader: to seamlessly connect societies, industries, and machines. It’s a holistic approach to a connected world, where the emphasis is not just on speed but on efficiency, reliability, and versatility.
5G vs. Its Predecessors
To understand the leap that 5G represents, it’s crucial to compare it with its predecessors:
- Speed: While 4G offers speeds up to 1 Gbps in its advanced versions, 5G promises speeds up to 20 Gbps. This means downloading a full-length HD movie in seconds rather than minutes.
- Latency: 4G’s latency can be around 30-50 milliseconds. In contrast, 5G aims for a latency as low as 1 millisecond, making real-time communication and remote control more efficient and reliable.
- Connection Density: 5G can support up to a million devices per square kilometer, a significant jump from 4G’s 100,000 devices. This is crucial for the proliferation of IoT devices.
Technical Underpinnings of 5G
5G’s prowess doesn’t just stem from better hardware but from a reimagined approach to network architecture:
- Network Slicing: One of the standout features of 5G is its ability to create ‘slices’ of the network tailored to specific needs. For instance, a slice for autonomous vehicles would prioritize low latency, while a slice for video streaming might focus on bandwidth.
- Edge Computing: Instead of relying solely on centralized data centers, 5G pushes computation to the ‘edge’—closer to where data is generated. This reduces latency and accelerates response times, especially vital for real-time applications.
- Beamforming: Traditional networks broadcast signals in all directions, leading to potential wastage. 5G, with its advanced antenna technology, can direct signals precisely where needed, enhancing efficiency and reducing interference.
The Global Impetus Behind 5G
The global enthusiasm for 5G isn’t just about consumer benefits. Industries see 5G as the backbone for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, where automation, AI, and real-time data analytics converge. From smart cities to precision agriculture, from augmented reality in education to remote surgeries in healthcare, the applications are boundless.
The Technical Aspects of 5G
New Radio Frequencies and Their Implications
The magic behind 5G’s impressive capabilities lies in its use of new radio frequencies. Unlike previous generations that operated on lower frequencies, 5G expands into the millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum, which ranges from 24 to 100 GHz. These higher frequencies can carry more data, leading to faster speeds. However, they come with their own set of challenges:
- Shorter Range: Higher frequencies have a shorter range, meaning they can’t travel as far as lower frequencies. This necessitates the deployment of more base stations or small cells to ensure coverage.
- Obstruction Issues: mmWave frequencies are more susceptible to interference from physical obstructions like buildings, trees, and even rain. This has led to the development of advanced antenna technologies to mitigate these challenges.
FR1 vs. FR2 Frequencies
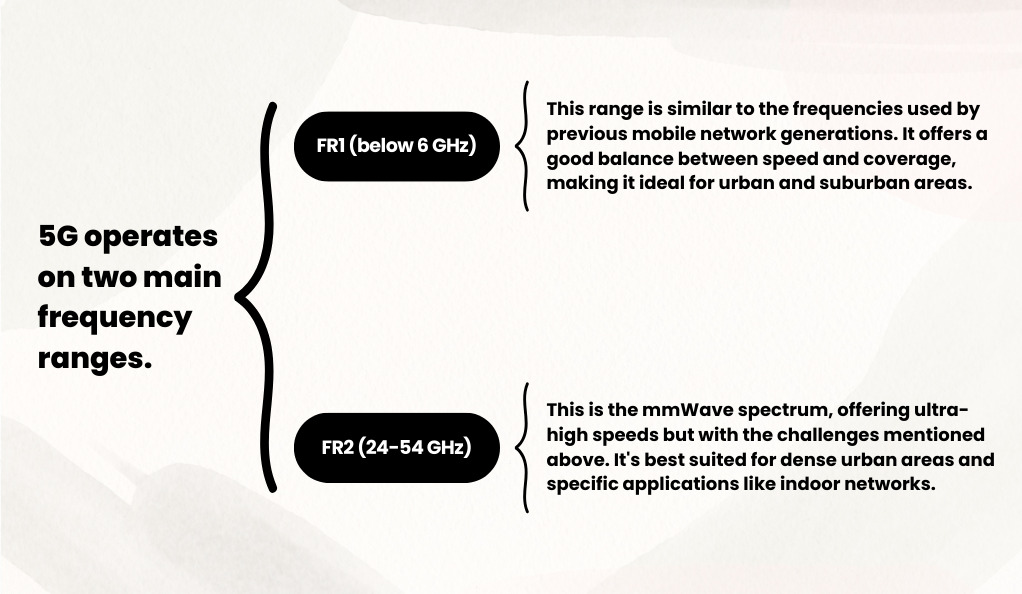
Challenges with Higher Frequencies
While the higher frequencies of 5G promise unprecedented speeds, they also present unique challenges:
- Infrastructure Overhaul: The shorter range of mmWave frequencies means that cities and towns need a denser network of base stations. This requires significant investment and infrastructure overhaul.
- Device Compatibility: Not all devices are equipped to handle the new frequencies, necessitating upgrades or replacements for users to benefit from 5G fully.
- Health Concerns: The use of higher frequencies has sparked debates about potential health implications. While extensive research indicates that 5G is safe, it’s essential to address these concerns transparently.
Innovative Solutions to Overcome Challenges
The telecom industry has been proactive in addressing the challenges posed by 5G’s technical aspects:
- Advanced Antenna Technologies: Techniques like beamforming and Massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) help direct signals more efficiently, overcoming the range and obstruction issues of higher frequencies.
- Network Densification: By deploying more small cells in strategic locations, providers can ensure consistent and reliable 5G coverage.
- Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS): This allows 5G to coexist with older networks by dynamically sharing the same frequency bands, ensuring a smoother transition.
5G and the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) represents a network of interconnected devices, from smart thermostats in our homes to sensors in industrial machinery. These devices collect and share data, making our lives more efficient and interconnected. The advent of 5G is set to supercharge this ecosystem, offering the speed, reliability, and capacity that IoT demands.
How 5G is Revolutionizing IoT
- Scalability: With its ability to support up to a million devices per square kilometer, 5G can accommodate the exponential growth of IoT devices.
- Low Latency: Real-time data processing is crucial for many IoT applications. With latencies as low as 1 millisecond, 5G ensures that devices can communicate and react in real-time.
- Reliability: 5G’s Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) ensures that critical IoT applications, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation, operate seamlessly without disruptions.
Real-world Applications and Benefits
- Smart Cities: With 5G-powered IoT, cities can optimize traffic flow, enhance public safety, manage energy consumption, and offer improved public services.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and even remote surgeries become feasible and reliable with 5G-enhanced IoT.
- Agriculture: Precision farming, where sensors monitor and respond to soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health in real-time, can lead to increased yields and sustainability.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles rely on vast amounts of data processed in real-time. 5G ensures these vehicles can communicate with each other and their surroundings, paving the way for safer and more efficient transportation systems.
Global Deployment and Adoption of 5G
The promise of 5G has ignited a global race among nations to deploy and capitalize on this transformative technology. Recognizing the potential economic, societal, and strategic advantages, countries are investing heavily in infrastructure, research, and development.
Current Status of 5G Deployment Worldwide
- Asia-Pacific: Led by South Korea, China, and Japan, the Asia-Pacific region has been at the forefront of 5G deployment. South Korea boasts one of the highest 5G penetration rates, while China is rapidly expanding its 5G infrastructure across its vast landscape.
- North America: The U.S. and Canada are making significant strides in 5G deployment, with major cities already experiencing the benefits and telecom giants investing billions in infrastructure.
- Europe: European nations, while initially slower in 5G adoption, are catching up. Countries like the UK, Germany, and Finland are leading the charge, with a focus on both urban and rural 5G accessibility.
- Rest of the World: Countries in regions like the Middle East, Africa, and Latin America are in varying stages of 5G adoption, with many recognizing the technology’s potential to leapfrog developmental challenges.
Countries Leading in 5G Adoption and Their Strategies

- South Korea: With a strategy focused on national coverage, collaboration between government and industry, and heavy investment in R&D, South Korea has emerged as a 5G leader.
- China: Leveraging its manufacturing prowess and vast market, China aims to be a dominant player in the 5G landscape. The government’s supportive policies and massive infrastructure projects underscore this ambition.
- United States: The U.S. approach is driven by private enterprise, with telecom giants like Verizon and AT&T competing to expand their 5G networks. The government, recognizing the strategic importance of 5G, is facilitating this through spectrum auctions and deregulation.
Conclusion
As we journey through the intricate tapestry of 5G technology, its undeniable impact on global communication becomes evident. From its technical nuances to its transformative potential for industries like IoT, 5G stands as a beacon of the next phase in our digital evolution. The global race to harness its power underscores its significance, with nations and industries recognizing its potential to redefine paradigms.
However, like any revolutionary technology, 5G is not without its challenges. From infrastructure costs to geopolitical tensions, the road to universal 5G adoption is paved with obstacles. Yet, the collective global effort to overcome these challenges speaks volumes about the world’s commitment to a more connected, efficient, and responsive future.
In essence, 5G is more than just a technological upgrade; it’s a symbol of human ambition and ingenuity. As we stand on the cusp of this new era, one thing is certain: the impact of 5G on global communication will be profound, reshaping our world in ways we are only beginning to imagine.